How Fast Can E-Bikes Go?
Electric bikes have surged in popularity as a convenient and eco-friendly mode of transportation. With their rising ubiquity on city streets and recreational trails, understanding their speed capabilities is crucial for both safety and optimal performance. This knowledge not only enhances the riding experience but also ensures compliance with regulations and promotes responsible usage.
Understanding E-Bike Speed
Explanation of Different Classes of E-Bikes
E-Bikes are categorized into three main classes, each with its own set of speed limitations and features:
Class 1 E-Bikes: These bikes have a maximum speed of 20 mph and provide assistance only when pedaling. They are suitable for beginners and casual riders seeking a gentle boost during their commute or leisure rides.
Class 2 E-Bikes: Similar to Class 1, these bikes also have a maximum speed of 20 mph but offer the option of throttle assistance without pedaling. Ideal for those who prefer a bit of extra power for starting off or tackling inclines.
Class 3 E-Bikes (Speed Pedelecs): With a maximum speed of 28 mph, Class 3 bikes are designed for more experienced riders. They offer faster speeds and are often equipped to handle urban commuting on busier roads.
Legal Limitations on E-Bike Speeds
While electric bikes provide a convenient means of transportation, riders must adhere to specific speed regulations:
Federal Regulations: According to federal law, electric bikes are classified as "low-speed electric bicycles" with a maximum speed of 20 mph on level surfaces. However, federal regulations do not specify a maximum assisted speed.
State and Local Laws: States may impose additional regulations on electric bike speeds, and riders must also comply with local speed limits for public roads and trails.
Consequences of Violating Speed Limits
Exceeding speed limits on electric bikes can result in penalties similar to those for motor vehicles, including fines and potential legal consequences. Additionally, tampering with the speed capabilities of electric bikes is illegal and may lead to further repercussions.
Factors Affecting E-Bike Speed
Motor Power and Type
The power and type of motor significantly influence an electric bike's speed. While motor power, measured in watts, affects acceleration, it doesn't directly impact top speed. Both rear hub and mid-drive motors contribute to the bike's speed capabilities.
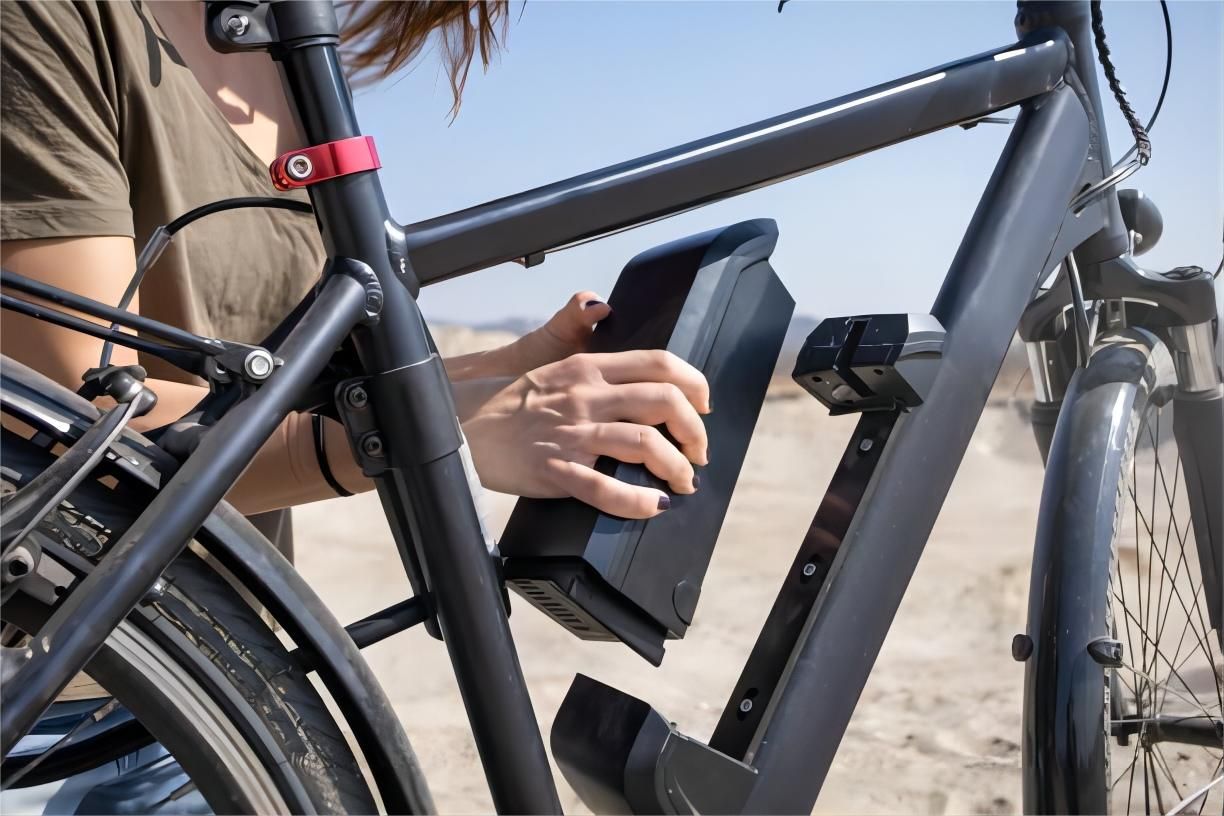
Battery Capacity
Battery capacity plays a crucial role in determining the riding range rather than speed. Larger battery sizes provide more fuel cells, allowing for longer distances on a single charge. However, they do not directly affect the bike's top speed.
Terrain and Road Conditions
The terrain and road conditions can impact electric bike speed. Climbing steep hills requires more power from both the rider and the motor, potentially reducing overall speed. Additionally, rough or uneven surfaces may affect the bike's stability and speed.
Rider Weight and Skill Level
The weight of the rider affects the bike's performance, as heavier individuals may require more power to propel the bike forward. Moreover, skilled riders can optimize their use of gears and pedaling techniques to maintain speed more efficiently.
Riding Mode
Most electric bikes offer multiple power modes that affect speed and effort required for pedaling. Selecting a higher power mode allows for faster riding with less exertion but may drain the battery more quickly. Conversely, lower power modes conserve battery life but require more physical effort from the rider.
Maximizing E-Bike Speed
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring your electric bike operates at peak performance. Keep the chain lubricated and free from debris, and maintain proper tire pressure to reduce rolling resistance and improve speed.
Monitoring Battery Charge Level
Keep track of your e-bike's battery charge level to avoid running out of power during your ride. Charge the battery fully before each ride and consider investing in a spare battery for longer journeys.
Selecting Appropriate Power Modes
Choose the power mode that best suits your riding needs and preferences. Higher power modes provide faster speeds with less effort but consume more battery power. Adjust the power mode based on terrain and desired riding speed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Top Speed of E-Bikes?
The top speed of electric bikes varies depending on factors such as class, motor power, and terrain. Class 1 electric bikes typically have a maximum speed of 20 mph, while Class 3 bikes can reach speeds of up to 28 mph.
Can E-Bikes Go Faster Than 20 mph?
In some cases, yes. Class 3 electric bikes are capable of reaching speeds beyond 20 mph, with a maximum assisted speed of 28 mph. However, riders should be aware of local regulations and ensure compliance with speed limits.
How Does Motor Wattage Affect E-Bike Speed?
Motor wattage primarily influences acceleration rather than top speed. A higher wattage motor can propel the bike to its maximum speed more quickly but does not necessarily increase the top speed, which is typically regulated by class and local laws.
What Are the Legal Implications of Modifying E-Bikes for Higher Speeds?
Modifying electric bikes to exceed legal speed limits can have serious legal consequences. Tampering with the speed capabilities of electric bikes may result in fines, penalties, and even the classification of the bike as a motor vehicle, subject to additional regulations.
Effective Use of Gears
Utilize your bike's gears to optimize speed and efficiency. Shift into lower gears when climbing hills to reduce strain on the motor and conserve battery power. Conversely, switch to higher gears when riding on flat terrain to maximize speed.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of electric bike speed is pivotal for a fulfilling riding experience. Whether you're navigating city streets or tackling off-road trails, being aware of factors like motor power, battery capacity, and legal limitations ensures both safety and enjoyment.
At MOVCAN, we are committed to providing high-quality electric bikes and accessories that cater to diverse riding needs. Our range of e-bikes offers versatility, durability, and cutting-edge technology to enhance your cycling adventures. Explore our collection of e-bikes and accessories, and embark on your next adventure with confidence and style.